In summary, if you need to list the users in a MySQL database, I hope this has been helpful. MySQL stores information about the users , in a table named user in the mysql database. As use can see, there are two users that are currently logged in the MySQL database, one is executing a query while the other is “sleep”. You shouldn’t be able to read the passwords.

MySQL user passwords are stored in a hashed form. The instructions should work with any modern Linux distribution such as Ubuntu 18. Depending on the MySQL or MariaDB server version you are running on your system, you will need to use different commands to change the user password. Once logged in use various SQL queries as follows to show users accounts in a MariaDB or MySQL database.
Unfortunately your user password is irretrievable. It has been hashed with a one way hash which if. MySQL account consists of two components: user and host. Each account includes the user ’s name and host.
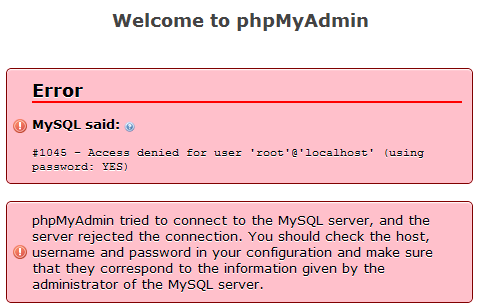
It should be different from the system root password. Once we are in the MySQL console as the root user , we can run sentences and commands. As a result, we will be able to see all the users that have been created.
This is a common practice for password storage for the sake of security. In MySQL , there are no commands SHOW USERS or LIST USERS. This tutorial explains how to create a user with password in MySQL. For information about MySQL native password hashing, see Section 6. Now, when you to MySQL , with the command mysql -u root -p, you will be prompted to enter the newly configured password. Password Hashing in MySQL ”. An alternative method for setting the root password for the first time, one that also adds a bit of security to your MySQL database, is to use the mysql _secure_connection command.
There’s lots of tables in your MySQL database, but right now we’ll only need the User table. Solution: MySQL add user and grant syntax. I have verified this approach with both MAMP and using MySQL on Linux servers. We can use ways, – mysqladmin, – linguagem SQL.
SHOW GRANTS FOR CURRENT_ USER (or any of the equivalent syntaxes) is used in DEFINER context, such as within a stored procedure that is defined with SQL SECURITY DEFINER), the grants displayed are those of the definer and not the invoker. SHOW GRANTS displays only the privileges granted explicitly to the named account. Secon specify the password for the user after the IDENTIFIED BY keywords. The IF NOT EXISTS option conditionally create a new user only if it does not exist. Note that the CREATE USER statement creates a new user without any privileges.
To grant privileges to the user , you use the GRANT statement. How do you change the user ’s password ? There are several ways to do this, one of which we can do without even entering the MySQL command console. A user is a database account that allows you to to the MySQL database.
MySQL has a PASSWORD () function, and the same scheme is used to encrypt your MySQL administrator password. Once you create a user , you then need to grant it permissions. One difference between MySQL and other database platforms is that the user and host name determine user permissions. Works best if you can connect to MySQL without a password. Output is formatted so it can be run in a MySQL shell.
Caution: Output also contains the MySQL root user permissions and password ! This is an aggregation of various StackOverflow posts, user tutorials, and official docs that helped me figure out how to reset my local MySQL root password. Thanks to an early engineering assignment, my initial database setup got really screwed up. To create a database user , type the following command.
While new MySQL software security features are always welcome, they can impact use and performance. Now by default, MySQL 5. In this blog, we’ll discuss how to find the MySQL 5. This will show all the tables that a user has access to.
Keine Kommentare:
Kommentar veröffentlichen
Hinweis: Nur ein Mitglied dieses Blogs kann Kommentare posten.